New intracellular “smoke detector” discovered
Study by the University of Bonn could lead to therapies against skin and intestinal diseases in the medium term
Researchers at the Universities of Bonn and Singapore have discovered a new intracellular “smoke detector.” The sensor warns of damage to the mitochondria – the microscopic power plants that supply the cell with energy. If it does not function properly, chronic skin diseases can result. The sensor may also be important for unimpaired heart and bowel function. The results have now been published in the journal Nature Immunology.
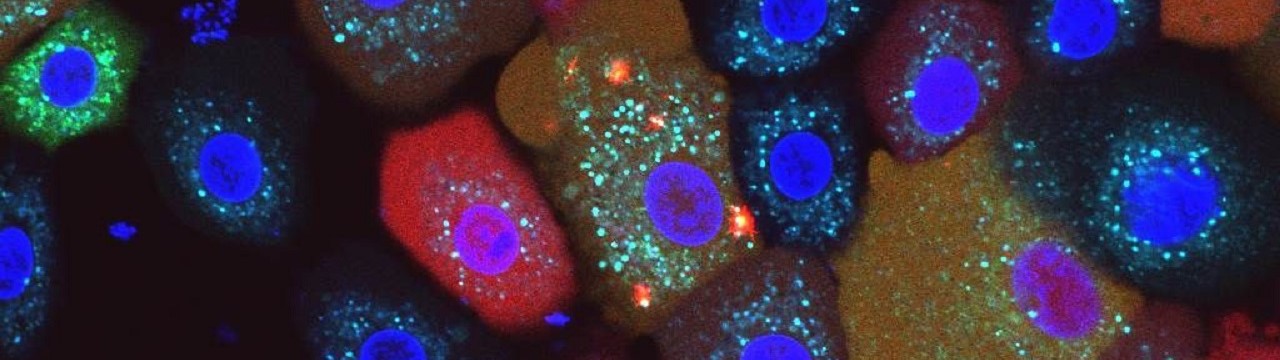
Every cell in the body has numerous sensors that monitor its function. Some sound the alarm after a virus attack, for instance; others kick in when any kind of damage threatens the cell’s survival. “We have now discovered that a molecule called NLRP10 also acts as a sensor,” explains Prof. Dr. Eicke Latz, head of the Institute of Innate Immunity at the University Hospital Bonn. “This was completely unknown until now.”
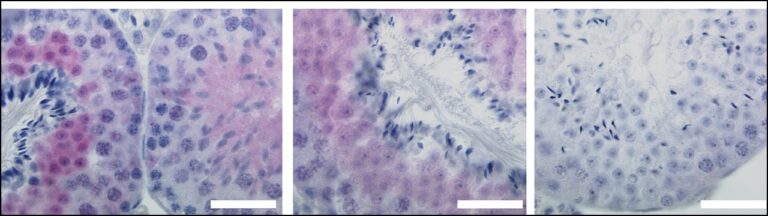
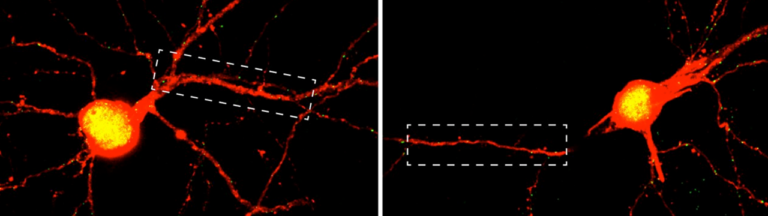
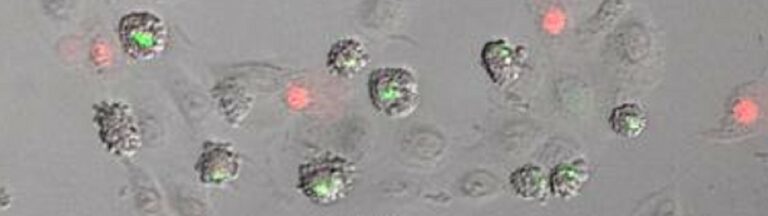
Figuratively speaking, NLRP10 detects when the mitochondria in the cell start to smoke due to some malfunction. These are the microscopic power plants that provide the energy for cellular functions. As soon as an NLRP10 sensor detects damage to mitochondria, it sets off a complicated process. This creates a so-called inflammasome, a complex molecular machine. Its activity ultimately causes the cell to perish and be disposed of by summoned immune cells.
“This process is hugely important,” explains Latz, who is also the spokesperson for the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 and a member of the Transdisciplinary Research Area “Life and Health” at the University of Bonn. This is because the inflammasome ensures that the fire is stamped out straight away, which prevents a prolonged smoldering fire that would damage other parts of the tissue. “Disruption of this mechanism can result in chronic inflammation,” the researcher emphasizes. “Killing cells with mitochondrial defects may sound drastic. Ultimately, however, this step prevents more serious consequences.” […]
Participating Core Facilities: The authors acknowledge the support from the Microscopy Core Facility.
Participating institutions and funding:
In addition to the University Hospital and the University of Bonn, the Skin Research Institute of Singapore, the Technical University of Dresden and the University of Hohenheim were involved in the work. The study was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), by EU funds under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 program, by the Helmholtz Association, and by the Nation Research Foundation in Singapore.
Publication: T. Próchnicki et al.: Mitochondrial damage activates the NLRP10 inflammasome; Nature Immunology;
DOI: 10.1038/s41590-023-01451-y