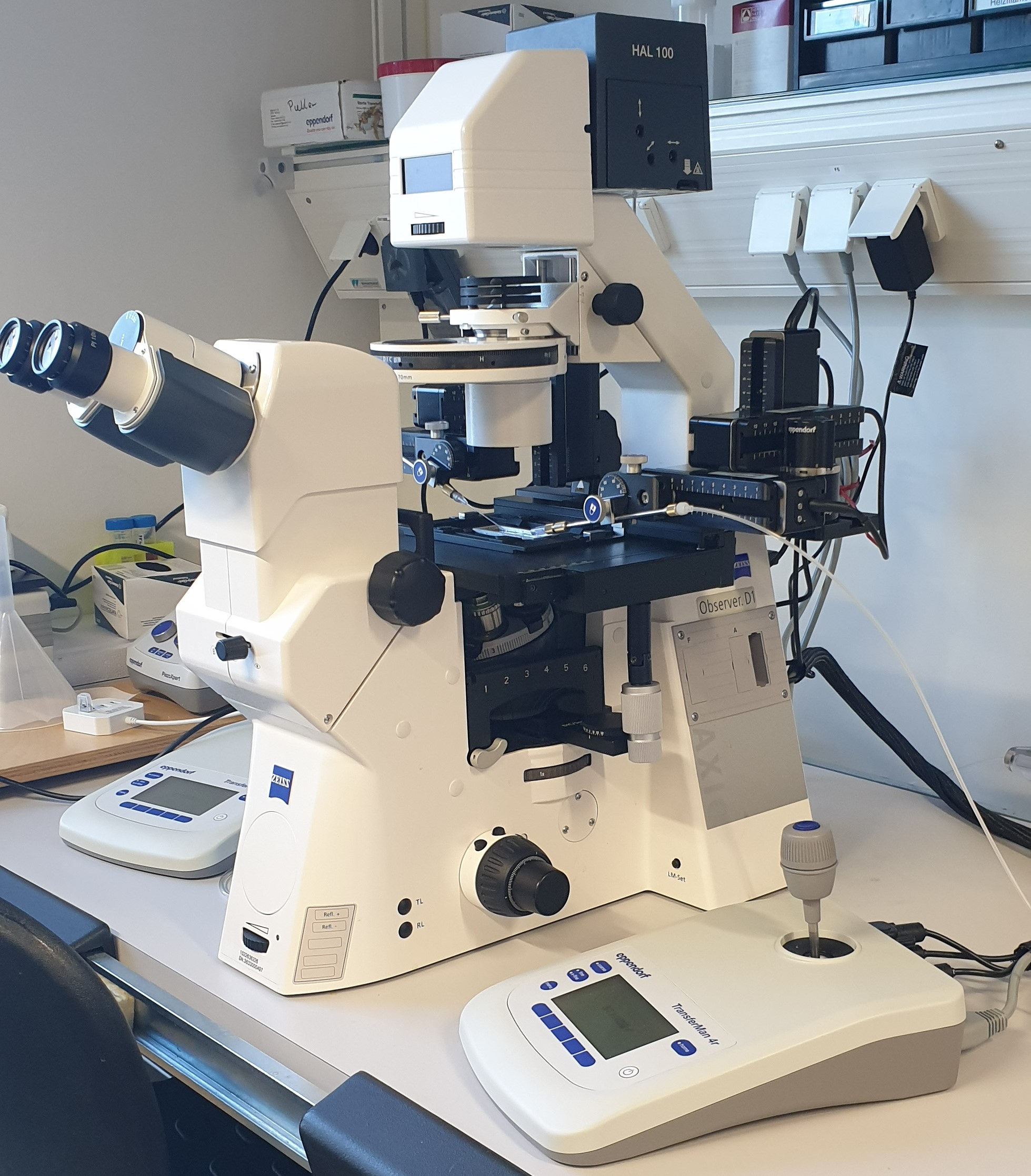
Injection set-up
Our facility operates a differential interference contrast microscope equipped with micro-manipulators, a Piezo element and a MICRO-ePORE™ Pinpoint Cell Penetrator. This setup applies for a variety of mouse embryo micro-manipulation techniques, including pronuclear injections into oocytes, 2-cell embryos as well as blastocyst injections.
Further we are equipped with an electroporation device, allowing for a fast and high-throughput manipulation of oocytes for an efficient and cost-effective generation of CRISPR/Cas9 gene-edited mice.
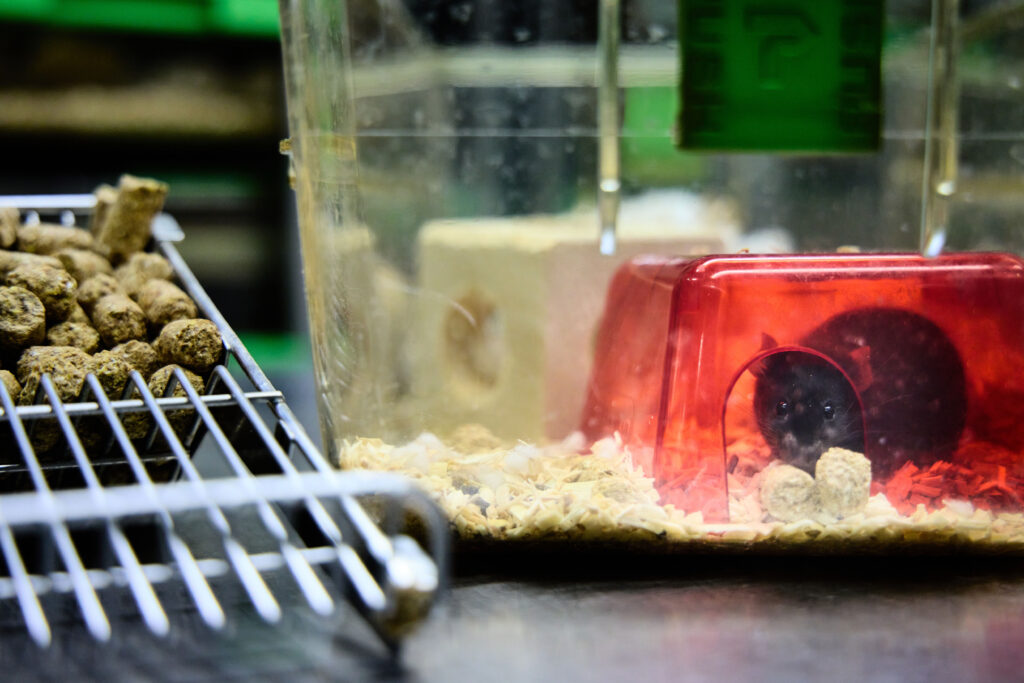

Mouse breeding facility
Micro-manipulated embryos are transferred into pseudo-pregnant foster mice, either by oviduct transfer of 2-cell stage embryos or by in utero transfer of blastocysts.
Our animal facility located at the University of Bonn, Campus Poppelsdorf was established in 2012 and meets all standards of a modern animal facility.
The facility is designed for breeding and housing of mice. Highest priority of our daily work is to keep our animals healthy. Therefore, we have a very strict hygiene management that includes daily desinfection of all floors, sterilization/autoclave/H2O2 treatment of all materials and items entering mouse rooms as well as three different hygiene barriers. In all barriers masks, gloves, hair cover and dedicated clothing/shoes are worn.
Mice from Gene-Editing and Transgenic projects are transferred into our red barrier. All mouse lines are brought into this area once by embryo transfer and breeding is maintained by mating. The mice are free of all relevant murine pathogens (see FELASA guideline 2014). To keep unwanted entry of microorganisms as low as possible barrier red is a high security air shower-in barrier with access for dedicated staff only.
Mice are housed in individually ventilated cages (IVC, Tecniplast) at 21 ± 2 °C, 55 ± 15 % relative humidity and an air exchange rate of fiftyfold – seventyfold per hour. Day and night are simulated with 12 h white light, 300 lx and 12 h red light. Each cage is equipped with autoclaved food and autoclaved water ad libitum as well as autoclaved wooden bedding and nesting material.
The health status of our colony is monitored every three months. One sentinel female per double-rack is tested for various murine pathogens (see FELASA guideline 2014) by a certified laboratory. The current health certificate of the red barrier can be viewed here.